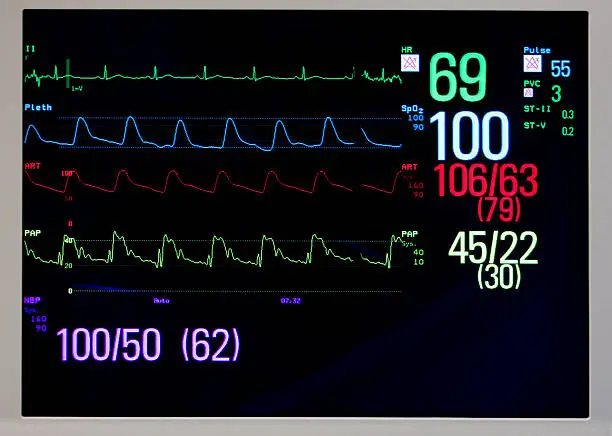
What is the use of Multipara Monitor?
Multipara Monitor is an electronic medical device made up of one or more monitoring sensors, one or more processing components, and a screen display (also known as a “Patient ICU Monitor”).that provides and records for medical professionals a patient’s medical vital signs (body temperature, blood pressure, pulse rate and respiratory
Monitoring Parameters List of Multipara Monitor :
- Saturation of Peripheral Oxygen (Spo2)
- Non Invasive Blood Pressure (NIBP)
- Invasive Blood Pressure
- Heart rate by ECG
- Respiration
- Temperature
1. Spo2 (Saturation of Peripheral Oxygen)
Unit: %
The proportion of oxyhemoglobin to the total amount of hemoglobin in the blood is known as oxygen saturation. Hemoglobin molecules are carriers of Oxygen in the Blood. It is a mixture of oxygen from the lungs and hemoglobin. Oxy-hemoglobin (HbO2) is the bright red hemoglobin
Technology:
The Pulse Oximetry Principle serves as the foundation for non-invasive PO2 measurement. It provides continuous and inexpensive monitoring of oxygen saturation. Red and infrared diodes with varying wavelengths are used by Spo2 probes to measure O2 levels.
Principle of Pulse Oximetry:
Beer’s Law:
The amount of light absorbed is proportional to the concentration of the light-absorbing substance
Lambert’s Law:
The amount of light absorbed is proportional to the length of the path that the light has to travel in the absorbing substance.
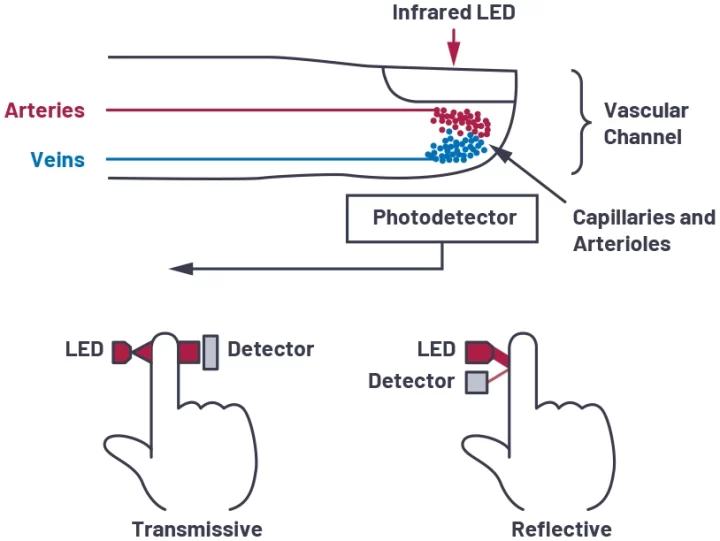
Normal range for SPO2: 95% to 100%
2. NIBP (Non Invasive Blood Pressure)
Unit: mmHg
Blood is delivered by arteries from the heart to numerous bodily locations. Blood pressure is the force of your blood against the artery walls. Throughout the day, your blood pressure typically increases and decreases.
Principle: Oscillometric
The Oscillometric approach is used in an automated method for measuring blood pressure while using an occluding cuff. The cuff automatically inflates to a predetermined value. Then, the pressure is gradually being reduced. The pressure wave creates oscillations in the vessel, which can be detected by the cuff.
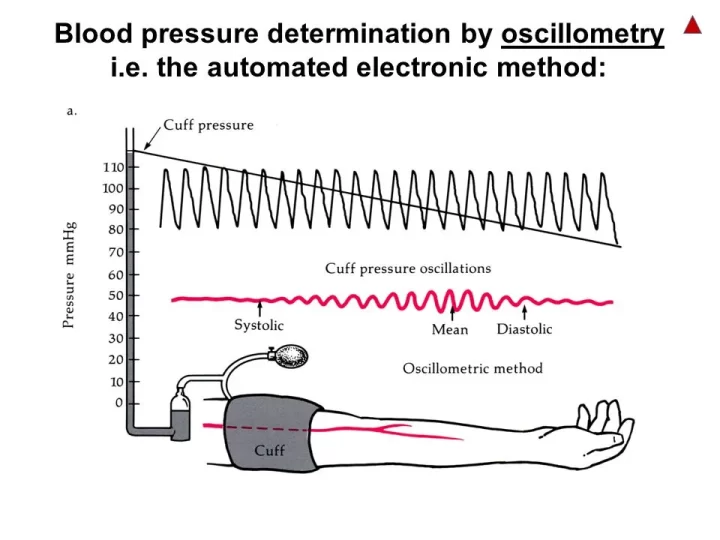
Systolic Blood pressure:
The pressure against the blood vessels during contraction of the heart is systolic blood pressure
Diastolic Blood pressure:
The pressure against the blood vessels during the Relaxation of the heart is Diastolic blood pressure Oscillometric technique uses sophisticated algorithms to determine MAP.
MAP : Mean Arterial pressure
The average pressure in a patient’s arteries during one cardiac cycle is known as MAP, or mean arterial pressure.
The formula shown below can be used to estimate the MAP.
- MAP = DP + 1/3(SP – DP) or
- MAP = DP + 1/3(PP) here PP= SP-DP
Normal Range for Blood pressure: 120/80 mmHg
3. Invasive blood pressure:
Unit: mmHg
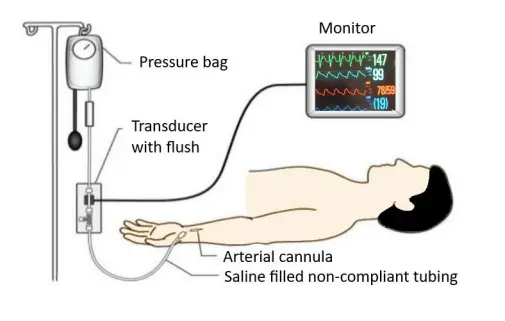
Invasive blood pressure monitoring:
The invasive (intra-arterial) blood pressure (IBP) monitoring technique is frequently utilised in the operating room as well as the intensive care unit (ICU).
By placing a cannula needle in the appropriate artery, this method directly measures the arterial pressure. A sterile, liquid-filled system that is linked to an electronic patient monitor is required to be connected to the cannula. Here the pressure of the saline is directly proportional to the pressure of the arterial blood. This method has the benefit of continuously monitoring a patient’s blood pressure beat-by-beat and displaying a waveform (a graph of pressure against time).
ECG (Electrocardiogram):
Patient monitors can perform continuous monitoring of Heart Rate by means of ECG The sequential Electrical activation of Heart Muscles results in P, QRS, and T waves in the ECG. The P-wave represents arterial depolarization(Contraction), the QRS complex represents Ventricular depolarization, and the T wave represents ventricular repolarization.
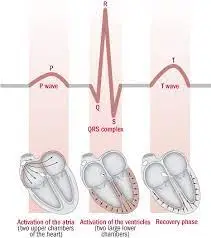
Heart rate measurement technique
Beat-to-beat calculation:
This is accomplished by measuring the time (T) between two consecutive pulses in seconds and converting that time into beats per minute,
using the formula beats/ min. = 60/T.
This method correctly depicts the true heart rate.
Sensors are limb or chest ECG electrodes.
Unit: bpm(beats per minute)
Normal Heart rate : 60 to 100 Beats per minute.
4. Respiration
Unit: bpm(breaths per minute)
The exchange of gases between the lungs and the atmosphere is known as respiration And is also called inhalation and exhalation of air-breathing.
Patient Monitors measure respiration through ECG electrodes By the chest wall movement.
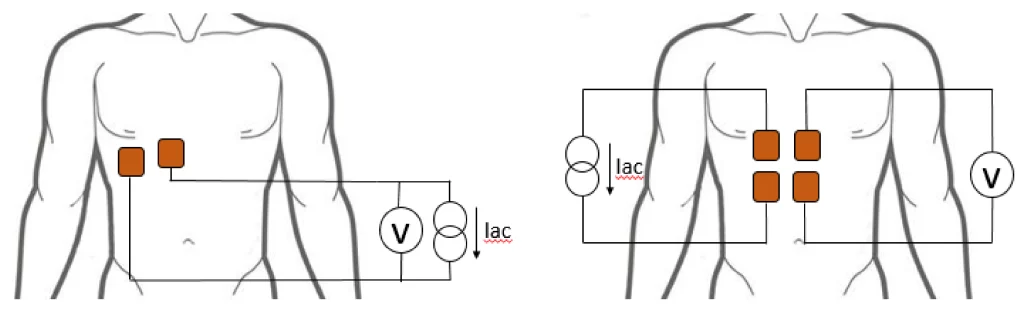
Principle: Impedance Pneumography
A common method for keeping track of someone’s breathing rate is called impedance pneumography. It is implemented by either using two electrodes or four electrodes. This method aims to quantify alterations in the electrical impedance of the thorax brought on by breathing or respiration.
Respiratory rate: It refers to the rate of breathing per minute. Respiration is Measured as Respiratory Rate (RR)
12 to 16 breaths per minute is considered a normal breathing rate.
5.TEMPERATURE:
The thermistor Principle provides the foundation for the monitor’s temperature monitoring. The thermistor with a negative temperature coefficient is typically used as the temperature sensor in multi-parameter monitors to measure body temperature since it has the property that its resistance value changes with temperature. High-end monitors can provide dual-channel body temperature in addition to providing single-channel body temperature. Surface probes and intracavitary probes are the two different kinds of body temperature sensors.
Normal Temperature: 98.6 F or (37º C)
Additional Measured Parameters:
It can be measured by adding additional modules to the monitor,
1. EtCO2: End-tidal Carbon Dioxide
The amount of carbon dioxide emitted at the end of an exhaled breath is known as end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2). It displays how well the blood transports carbon dioxide (CO2) back to the lungs for exhalation.
2. Cardiac Output:
Cardiac output is the amount of blood that is pumped out of each ventricle each minute.